


Posture is a critical aspect of overall health and fitness, as it plays a crucial role in how your body moves, functions, and feels. A good posture not only makes you look confident and attractive, but it also helps to prevent pain, injury, and chronic health conditions. On the other hand, poor posture can result in a host of problems, including neck and back pain, headaches, fatigue, and even respiratory difficulties.
The longer you are in a poor posture, the more time it takes to correct for it. Additionally, poor posture is sometimes caused by genetic challenges. If you have any questions, it is best to see a chiropractor.
In this article, we’ll explore how to assess your posture and identify any muscle imbalances that may be contributing to poor posture.
How do you know if your posture is good?
- Alignment of the spine: Stand in front of a mirror and look at your spine from the side. Your spine should have a natural S-shape with a slight curve in your lower back, a curve in your upper back, and your neck should be in a neutral position.
- Balance: Stand on one foot and see if you can maintain your balance without swaying. Repeat on the other foot. If you can’t maintain your balance, it could be a sign of poor posture.
- Comfort: Good posture should feel comfortable and natural. If you have to strain or feel discomfort to maintain your posture, it may be a sign that you are forcing yourself into an unnatural position.
- Pain or discomfort: If you experience pain or discomfort in your neck, shoulders, back, or hips, it may be a sign that your posture is poor.
- Posture assessments: Below is how you can evaluate your own posture. You can also get a posture assessment from a physical therapist or chiropractor.
Evaluating Your Posture



The first step in correcting any muscle imbalances related to posture is to assess your posture. A simple way to do this is to stand with your back against a wall and assess the position of your head, neck, shoulder blades, lower back, and pelvis. If your head, neck, and shoulders are not in a straight line with the wall, you may have a kyphosis-lordosis posture. If the wall is not touching your lower back, you have a flat-back posture, and if your pelvis tilts forward, it indicates a sway-back posture.
Posture Types
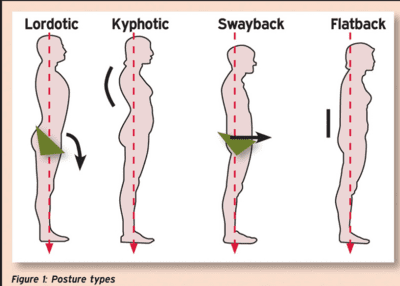


Kyphosis-Lordosis Posture
Kyphosis-lordosis posture is characterized by an exaggerated curvature of the upper back and a pronounced arch in the lower back. This posture can result in upper and lower back pain, headaches, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in your upper and lower back, as well as the core muscles.
Some exercises to help correct kyphosis-lordosis posture include:
- Cat-Cow Stretch: This stretch helps to improve mobility in the spine and strengthen the back muscles.
- Superman Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the upper and lower back, as well as the core muscles.
- Child’s Pose: This yoga pose helps to stretch and lengthen the muscles in the back and hips.
Flat-Back Posture
Flat-back posture is characterized by a lack of curvature in the lower back and an overall flattened appearance. This posture can result in lower back pain, hip pain, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Some exercises to help correct flat-back posture include:
- Pelvic Tilts: This exercise helps to activate the muscles in the lower back and hips.
- Plank: This exercise strengthens the core muscles and helps to improve posture.
- Bridge Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Sway-Back Posture
Sway-back posture is characterized by a tilt in the pelvis, which results in an exaggerated arch in the lower back. This posture can result in lower back pain, hip pain, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Some exercises to help correct sway-back posture include:
- Glute Bridge: This exercise targets the muscles in the lower back, hips, and glutes.
- Squats: This exercise helps to strengthen the muscles in the lower back, hips, and legs.
- Clamshell Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the hips and glutes.
By assessing your posture and identifying any muscle imbalances, you can design an effective fitness program to improve your posture.
Editor's Pick



Posture is a critical aspect of overall health and fitness, as it plays a crucial role in how your body moves, functions, and feels. A good posture not only makes you look confident and attractive, but it also helps to prevent pain, injury, and chronic health conditions. On the other hand, poor posture can result in a host of problems, including neck and back pain, headaches, fatigue, and even respiratory difficulties.
The longer you are in a poor posture, the more time it takes to correct for it. Additionally, poor posture is sometimes caused by genetic challenges. If you have any questions, it is best to see a chiropractor.
In this article, we’ll explore how to assess your posture and identify any muscle imbalances that may be contributing to poor posture.
How do you know if your posture is good?
- Alignment of the spine: Stand in front of a mirror and look at your spine from the side. Your spine should have a natural S-shape with a slight curve in your lower back, a curve in your upper back, and your neck should be in a neutral position.
- Balance: Stand on one foot and see if you can maintain your balance without swaying. Repeat on the other foot. If you can’t maintain your balance, it could be a sign of poor posture.
- Comfort: Good posture should feel comfortable and natural. If you have to strain or feel discomfort to maintain your posture, it may be a sign that you are forcing yourself into an unnatural position.
- Pain or discomfort: If you experience pain or discomfort in your neck, shoulders, back, or hips, it may be a sign that your posture is poor.
- Posture assessments: Below is how you can evaluate your own posture. You can also get a posture assessment from a physical therapist or chiropractor.
Evaluating Your Posture



The first step in correcting any muscle imbalances related to posture is to assess your posture. A simple way to do this is to stand with your back against a wall and assess the position of your head, neck, shoulder blades, lower back, and pelvis. If your head, neck, and shoulders are not in a straight line with the wall, you may have a kyphosis-lordosis posture. If the wall is not touching your lower back, you have a flat-back posture, and if your pelvis tilts forward, it indicates a sway-back posture.
Posture Types



Kyphosis-Lordosis Posture
Kyphosis-lordosis posture is characterized by an exaggerated curvature of the upper back and a pronounced arch in the lower back. This posture can result in upper and lower back pain, headaches, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in your upper and lower back, as well as the core muscles.
Some exercises to help correct kyphosis-lordosis posture include:
- Cat-Cow Stretch: This stretch helps to improve mobility in the spine and strengthen the back muscles.
- Superman Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the upper and lower back, as well as the core muscles.
- Child’s Pose: This yoga pose helps to stretch and lengthen the muscles in the back and hips.
Flat-Back Posture
Flat-back posture is characterized by a lack of curvature in the lower back and an overall flattened appearance. This posture can result in lower back pain, hip pain, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Some exercises to help correct flat-back posture include:
- Pelvic Tilts: This exercise helps to activate the muscles in the lower back and hips.
- Plank: This exercise strengthens the core muscles and helps to improve posture.
- Bridge Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Sway-Back Posture
Sway-back posture is characterized by a tilt in the pelvis, which results in an exaggerated arch in the lower back. This posture can result in lower back pain, hip pain, and decreased mobility. To correct this posture, it’s important to focus on strengthening the muscles in the lower back, hips, and core.
Some exercises to help correct sway-back posture include:
- Glute Bridge: This exercise targets the muscles in the lower back, hips, and glutes.
- Squats: This exercise helps to strengthen the muscles in the lower back, hips, and legs.
- Clamshell Exercise: This exercise targets the muscles in the hips and glutes.
By assessing your posture and identifying any muscle imbalances, you can design an effective fitness program to improve your posture.








Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?