The Importance of Metabolism in Fat Loss
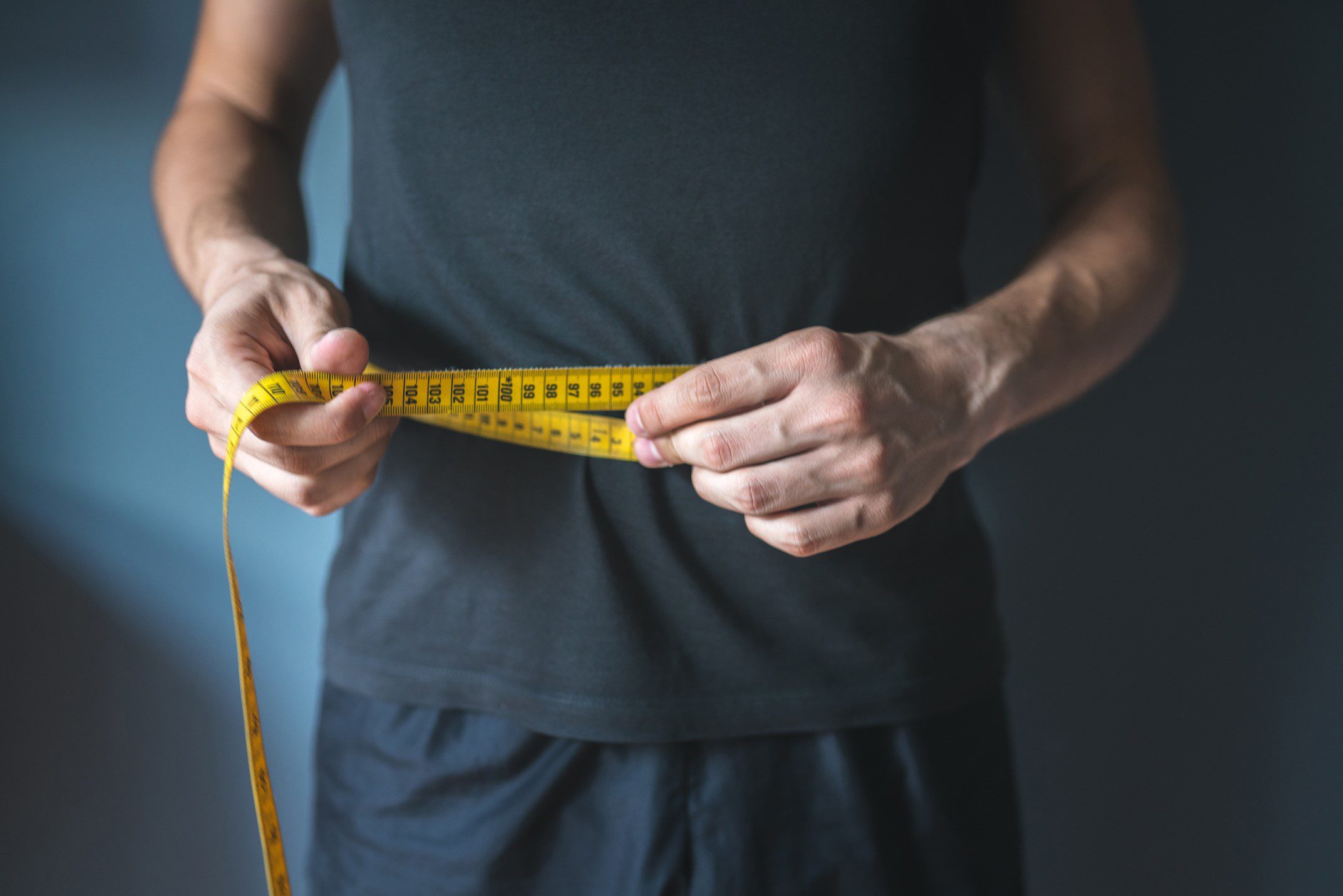
Metabolism is the process through which your body converts food into energy. It is a complex biochemical process that involves breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into molecules your body can use for various functions such as movement, cellular processes, and maintaining body temperature.
The importance of metabolism in fat loss cannot be overstated. A faster metabolism means you burn more calories at rest, even when not exercising.
This is because your body requires energy to perform essential functions, such as breathing, digesting food, circulating blood, and repairing cells. By increasing your metabolic rate, you can burn more calories throughout the day, which can lead to fat loss over time.
What Is Metabolism?
Metabolism can be divided into two main categories – catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules (such as carbohydrates or fats) into smaller ones to release energy.
On the other hand, anabolism refers to synthesizing complex molecules (such as proteins or nucleic acids) from smaller ones using energy. Several factors, including your age, gender, genetics, body size/composition, and lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise habits, influence your metabolic rate.
The Role of Diet in Boosting Metabolism
Diet plays a crucial role in boosting metabolism. Certain foods are known to increase metabolic rate due to their thermogenic properties – meaning they require more energy for digestion than other foods. Protein-rich foods such as chicken breast or tofu require more digestion energy than processed carbohydrates like white bread or pasta.
Similarly, fiber-rich foods like fruits or vegetables also require more energy for digestion due to their high fiber content. This is because your body cannot digest fiber and must work harder to break it down into its components.
Moreover, a balanced diet rich in all macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) can help regulate hormones such as insulin which play a crucial role in metabolism. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and can stimulate fat storage if it is consistently high due to consuming too much sugar or processed carbohydrates.
The Role of Exercise in Boosting Metabolism
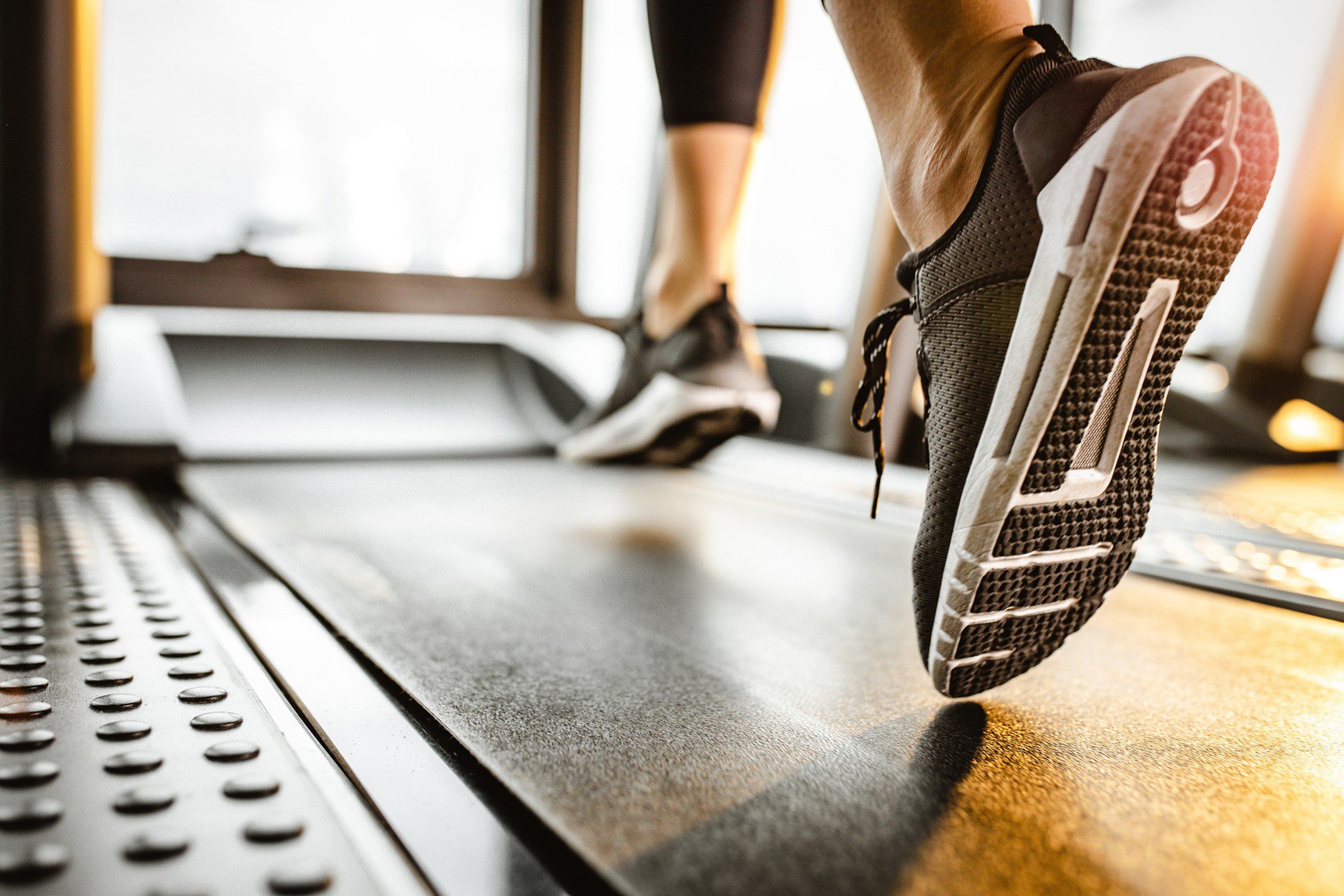
Exercise is another key factor in increasing metabolic rate. When you exercise, you burn calories during the actual activity and after you finish working out.
This is the after-burn effect or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). The type of exercise you choose also plays a role in boosting metabolism.
Resistance training such as weightlifting has been shown to increase muscle mass, increasing resting metabolic rate since muscle requires more energy than fat for maintenance. Cardiovascular exercises such as running or cycling can also increase metabolic rate since they need much power to perform, especially at high intensities.
Combining Diet and Exercise for Effective Fat Loss
While both diet and exercise are effective on their own, combining them leads to even better results when it comes to fat loss. By creating a caloric deficit through eating less and/or burning more calories through exercise, you force your body to tap into stored fat for energy.
However, it’s important to note that any drastic changes should be made gradually rather than all at once. Consistency is critical when achieving long-term fat loss goals since sustainable habits take time to develop.
Understanding metabolism can help guide your approach toward effective fat-loss strategies by leveraging the power of diet and exercise. Making small changes over time and being consistent can achieve your desired body composition and health goals.
The Body’s Engine: Understanding Metabolism
Overview of the Different Types of Metabolism
Metabolism is a term used to describe all the chemical reactions that occur in the body to maintain life. There are two main types of metabolism: catabolism and anabolism.
Catabolism refers to processes that break down complex molecules into smaller ones, while anabolism relates to methods that build larger molecules from smaller ones. Regarding weight loss and fat burning, however, focusing on another type of metabolism – basal metabolic rate (BMR) is essential.
BMR is the rate at which your body burns calories while at rest, accounting for most calories burned daily. Understanding your BMR is essential for knowing how many calories you must consume daily.
Factors That Affect Metabolism
Several factors can affect metabolism, such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Age plays a significant role in metabolism. As we age, our muscle mass decreases and body fat increases.
This means our BMR decreases since muscle requires more energy than fat. Gender also affects metabolism as men generally have higher muscle mass and lower body fat percentage than women due to hormonal differences.
This means that men typically have a higher BMR than women. Genetics also plays a role in determining metabolism since some people are born with naturally faster or slower metabolic rates than others.
Lifestyle choices such as exercise habits and diet also affect metabolism. Regular exercise can increase muscle mass and BMR while consuming too many processed foods or insufficient nutrients can slow the metabolic rate.
The Role of Hormones in Regulating Metabolism
Hormones play a critical role in regulating metabolism by controlling hunger levels, digestion processes, and energy expenditure. For example, the hormone leptin helps to regulate appetite and energy balance by signaling to the brain when the body has had enough food.
Insulin is another hormone that regulates metabolism by controlling blood sugar levels and promoting fat storage. An imbalance in hormones, such as an underactive thyroid gland, can cause a slow metabolism, leading to weight gain.
Hormonal imbalances can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, or other medical interventions. Understanding metabolism is essential for anyone looking to lose or maintain a healthy body weight.
Factors such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle choices all affect metabolic rate. Hormones also have an essential role in regulating metabolism and managing hormonal imbalances is crucial for maintaining optimal metabolic function.
Diet and Metabolism
Overview of Macronutrients and Their Impact on Metabolism
When it comes to metabolism, macronutrients play a significant role. Macronutrients are dietary components that provide energy, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients affects metabolism differently.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used to fuel the body’s cells.
The body will use this glucose for immediate energy needs or store it as glycogen in the liver or muscles to be utilized later. Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to excess glucose being stored as fat.
Proteins are essential in metabolism, specifically in muscle growth and repair. When consumed, proteins are broken down into amino acids and used by the body for various functions, such as building enzymes and hormones.
Additionally, protein has a higher thermic effect than either carbs or fat; this means that consuming protein requires more energy from the body to digest, which increases the metabolic rate slightly. Fats provide long-term energy storage for the body but have a little immediate impact on metabolic rate when consumed in reasonable amounts compared to carbs or protein.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Optimal Metabolic Function
A balanced diet is essential for optimal metabolic function because each macronutrient plays a critical role in ensuring your metabolism functions correctly.
Unfortunately, most people consume more carbohydrates than their bodies need while not eating enough protein or healthy fats (such as omega-3 fatty acids), which can harm their metabolism over time. A balanced diet should consist of 45-65% carbs (primarily complex), 20-35% healthy fats, and 10-35% protein.
Specific Foods That Can Boost Metabolism
While a balanced diet is critical, some specific foods can help boost metabolism. Green tea contains catechins which can help increase metabolic rate. Chili peppers contain capsaicin, which has been shown to increase energy expenditure during exercise by raising body temperature slightly.
Additionally, whole grains are high in fiber and have a lower glycemic index than refined grains, meaning that they will not spike blood sugar as much and require more energy to digest. Consuming these foods and other healthy foods can significantly boost the metabolism and lead to increased fat loss over time.
Balanced diet is essential
A balanced diet is essential for optimal metabolic function. Consuming the right amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can ensure your body functions correctly.
Additionally, consuming specific foods such as green tea, chili peppers, and whole grains can provide an extra boost to metabolic rate, which helps with weight loss goals. Remember that small dietary changes over time lead to more significant results.
Exercise and Metabolism
When it comes to boosting metabolism, exercise is a powerful tool that can help increase your metabolic rate and burn more calories. Exercise not only burns calories during the activity but also helps to build muscle mass, which increases your basal metabolic rate (BMR).
BMR refers to the number of calories your body burns at rest. The more muscle mass you have, the higher your BMR will be, which means you will burn more calories even when not exercising.
Explanation of how exercise affects metabolism
During exercise, your body uses energy to fuel the activity. This energy comes from the food you eat in the form of glucose stored in muscles or glycogen stored in the liver and muscle tissue.
When this energy source is depleted during exercise, your body turns to stored fat for fuel, leading to fat loss. Regular exercise also stimulates the production of hormones such as testosterone which helps boost metabolic rate and aids weight loss.
The effect of exercise on metabolism varies based on factors such as age, fitness level, and type of activity performed. However, studies show that even moderate-intensity aerobic activity can increase metabolic rate several hours after exercising.
Types of exercises that are most effective for boosting metabolic rate
Not all types of exercises are created equal for boosting metabolism. Some varieties are more effective in burning calories and building muscle mass. Aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, or swimming is great for burning calories during physical exertion. In contrast, resistance training, like weightlifting, burns calories and builds lean muscle mass, increasing BMR even while resting.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is another type of workout that is highly effective in increasing metabolism long after the workout. HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest.
The benefits of strength training for increasing muscle mass
Strength training is an important component of any exercise program. It involves using weights or resistance to build muscle mass and increase overall strength.
The benefits of strength training go beyond just aesthetics- it can also help to increase metabolic rate, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of injury during physical activity. An effective strength-training program should include a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups in your body.
These can include squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows. Regularly performing these exercises with proper form and technique can build lean muscle mass, which will help increase metabolism and burn more calories even at rest.
Exercising regularly is an excellent way to boost metabolism by burning calories during the activity and building lean muscles, which increases BMR even while at rest. Resistance training like weightlifting and HIIT are instrumental in achieving this goal as they are highly effective in building muscle mass while burning calories.
Combining Diet & Exercise for Fat Loss
The Importance of Creating a Caloric Deficit through Diet and Exercise to Achieve Fat Loss
Fat loss is achieved by creating a caloric deficit, meaning consuming fewer calories than the body requires to function. This deficit can be made through both diet and exercise.
A combination of both will yield the best results. The human body requires energy to exist, called basal metabolic rate (BMR).
BMR accounts for about 60-70% of daily caloric expenditure. Additional calories are burned through everyday activities such as walking, exercising, and other physical activities.
By creating a caloric deficit, the body is forced to draw on stored fat for energy, leading to fat loss. The recommended daily calorie intake varies based on age, gender, activity level, and muscle mass.
Generally speaking, women require between 1200-2000 calories per day depending on their activity level, while men require between 1500-2500 calories per day depending on their activity level. Reducing calorie intake by 500-1000 calories per day can result in a weight loss of one to two pounds per week.
To create a caloric deficit through exercise, choose activities that burn more calories, such as HIIT workouts or resistance training, rather than low-intensity steady-state (LISS) exercises like walking or jogging. Resistance training helps build lean muscle mass, which increases metabolism helping with long-term weight management.
How to Create a Sustainable Plan that Includes Both Diet and Exercise to Maximize Results
Sustainable weight loss requires choosing a healthy and satisfying eating plan, along with incorporating regular physical activity into your routine. Focusing on short-term and long-term goals is essential when developing a sustainable program.
Start by using an online calculator to determine how many total calories you need each day. Once you have that number, you can calculate your caloric deficit by subtracting 500-1000 calories per day from that number.
Next, plan meals and snacks for the week ahead to ensure you stay within your target calorie range. Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates while avoiding processed or high-calorie foods.
Regarding exercise, aim for at least 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week and strength training at least two days per week. Schedule workouts in advance and treat them like appointments to ensure consistency.
The Role of Consistency in Achieving Long-Term Fat Loss Goals
Consistency is key when it comes to achieving long-term fat loss goals. Even with a well-designed plan, if followed consistently over time, weight loss results will be manageable to obtain or maintain.
Develop habits like meal prepping on weekends or tracking calories using an app to stay consistent with diet goals. When dining out, choose wisely; select options that fit your caloric intake rather than higher calorie choices.
For exercise consistency, create an environment that encourages physical activity; ensure workout clothes are clean and readily available; and set up a designated spot for exercise equipment at home. Also, including accountability partners like a gym buddy or hiring a personal trainer can help make the process more enjoyable while keeping you on track.
Understanding the role of metabolism is crucial
Overall, understanding the role of metabolism in fat loss is crucial for anyone looking to improve their overall health and well-being. While diet and exercise are both critical factors, it’s important to remember that they work together to create a sustainable plan to help you achieve your goals. By incorporating a balanced diet focusing on whole foods and regular exercise that includes cardiovascular activity and strength training, you can boost your metabolism and create a caloric deficit necessary for fat loss.
Consistency is critical when it comes to achieving long-term results. It’s important to remember that small changes over time can significantly improve overall health and body composition.
Don’t expect overnight success but know that every positive step will bring you closer to your goals. There is no magic pill or quick fix for achieving fat loss.
To truly see sustainable results, focus on creating a lifestyle plan with a balanced diet and regular exercise routine. By making these changes over time, you will achieve your desired body composition and improve your overall health and well-being.
Remember: You Got This!
It’s easy to become overwhelmed with all the information about weight loss, diets, supplements, etc. But don’t let this discourage you! Remember why you started in the first place – whether for health reasons or just wanting to look better in your favorite pair of jeans – keep this goal at the forefront of your mind.
You have all the tools necessary for success – motivation, knowledge about metabolism & diet/exercise strategies- so keep pushing forward! Every day presents an opportunity for improvement- whether trying new foods or increasing the intensity of your workout regimen – so embrace the journey toward optimal health & wellness!
Editor's Pick



The Importance of Metabolism in Fat Loss
Metabolism is the process through which your body converts food into energy. It is a complex biochemical process that involves breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into molecules your body can use for various functions such as movement, cellular processes, and maintaining body temperature.
The importance of metabolism in fat loss cannot be overstated. A faster metabolism means you burn more calories at rest, even when not exercising.
This is because your body requires energy to perform essential functions, such as breathing, digesting food, circulating blood, and repairing cells. By increasing your metabolic rate, you can burn more calories throughout the day, which can lead to fat loss over time.
What Is Metabolism?
Metabolism can be divided into two main categories – catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules (such as carbohydrates or fats) into smaller ones to release energy.
On the other hand, anabolism refers to synthesizing complex molecules (such as proteins or nucleic acids) from smaller ones using energy. Several factors, including your age, gender, genetics, body size/composition, and lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise habits, influence your metabolic rate.
The Role of Diet in Boosting Metabolism
Diet plays a crucial role in boosting metabolism. Certain foods are known to increase metabolic rate due to their thermogenic properties – meaning they require more energy for digestion than other foods. Protein-rich foods such as chicken breast or tofu require more digestion energy than processed carbohydrates like white bread or pasta.
Similarly, fiber-rich foods like fruits or vegetables also require more energy for digestion due to their high fiber content. This is because your body cannot digest fiber and must work harder to break it down into its components.
Moreover, a balanced diet rich in all macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) can help regulate hormones such as insulin which play a crucial role in metabolism. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and can stimulate fat storage if it is consistently high due to consuming too much sugar or processed carbohydrates.
The Role of Exercise in Boosting Metabolism
Exercise is another key factor in increasing metabolic rate. When you exercise, you burn calories during the actual activity and after you finish working out.
This is the after-burn effect or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). The type of exercise you choose also plays a role in boosting metabolism.
Resistance training such as weightlifting has been shown to increase muscle mass, increasing resting metabolic rate since muscle requires more energy than fat for maintenance. Cardiovascular exercises such as running or cycling can also increase metabolic rate since they need much power to perform, especially at high intensities.
Combining Diet and Exercise for Effective Fat Loss
While both diet and exercise are effective on their own, combining them leads to even better results when it comes to fat loss. By creating a caloric deficit through eating less and/or burning more calories through exercise, you force your body to tap into stored fat for energy.
However, it’s important to note that any drastic changes should be made gradually rather than all at once. Consistency is critical when achieving long-term fat loss goals since sustainable habits take time to develop.
Understanding metabolism can help guide your approach toward effective fat-loss strategies by leveraging the power of diet and exercise. Making small changes over time and being consistent can achieve your desired body composition and health goals.
The Body’s Engine: Understanding Metabolism
Overview of the Different Types of Metabolism
Metabolism is a term used to describe all the chemical reactions that occur in the body to maintain life. There are two main types of metabolism: catabolism and anabolism.
Catabolism refers to processes that break down complex molecules into smaller ones, while anabolism relates to methods that build larger molecules from smaller ones. Regarding weight loss and fat burning, however, focusing on another type of metabolism – basal metabolic rate (BMR) is essential.
BMR is the rate at which your body burns calories while at rest, accounting for most calories burned daily. Understanding your BMR is essential for knowing how many calories you must consume daily.
Factors That Affect Metabolism
Several factors can affect metabolism, such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Age plays a significant role in metabolism. As we age, our muscle mass decreases and body fat increases.
This means our BMR decreases since muscle requires more energy than fat. Gender also affects metabolism as men generally have higher muscle mass and lower body fat percentage than women due to hormonal differences.
This means that men typically have a higher BMR than women. Genetics also plays a role in determining metabolism since some people are born with naturally faster or slower metabolic rates than others.
Lifestyle choices such as exercise habits and diet also affect metabolism. Regular exercise can increase muscle mass and BMR while consuming too many processed foods or insufficient nutrients can slow the metabolic rate.
The Role of Hormones in Regulating Metabolism
Hormones play a critical role in regulating metabolism by controlling hunger levels, digestion processes, and energy expenditure. For example, the hormone leptin helps to regulate appetite and energy balance by signaling to the brain when the body has had enough food.
Insulin is another hormone that regulates metabolism by controlling blood sugar levels and promoting fat storage. An imbalance in hormones, such as an underactive thyroid gland, can cause a slow metabolism, leading to weight gain.
Hormonal imbalances can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, or other medical interventions. Understanding metabolism is essential for anyone looking to lose or maintain a healthy body weight.
Factors such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle choices all affect metabolic rate. Hormones also have an essential role in regulating metabolism and managing hormonal imbalances is crucial for maintaining optimal metabolic function.
Diet and Metabolism
Overview of Macronutrients and Their Impact on Metabolism
When it comes to metabolism, macronutrients play a significant role. Macronutrients are dietary components that provide energy, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients affects metabolism differently.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used to fuel the body’s cells.
The body will use this glucose for immediate energy needs or store it as glycogen in the liver or muscles to be utilized later. Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to excess glucose being stored as fat.
Proteins are essential in metabolism, specifically in muscle growth and repair. When consumed, proteins are broken down into amino acids and used by the body for various functions, such as building enzymes and hormones.
Additionally, protein has a higher thermic effect than either carbs or fat; this means that consuming protein requires more energy from the body to digest, which increases the metabolic rate slightly. Fats provide long-term energy storage for the body but have a little immediate impact on metabolic rate when consumed in reasonable amounts compared to carbs or protein.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Optimal Metabolic Function
A balanced diet is essential for optimal metabolic function because each macronutrient plays a critical role in ensuring your metabolism functions correctly.
Unfortunately, most people consume more carbohydrates than their bodies need while not eating enough protein or healthy fats (such as omega-3 fatty acids), which can harm their metabolism over time. A balanced diet should consist of 45-65% carbs (primarily complex), 20-35% healthy fats, and 10-35% protein.
Specific Foods That Can Boost Metabolism
While a balanced diet is critical, some specific foods can help boost metabolism. Green tea contains catechins which can help increase metabolic rate. Chili peppers contain capsaicin, which has been shown to increase energy expenditure during exercise by raising body temperature slightly.
Additionally, whole grains are high in fiber and have a lower glycemic index than refined grains, meaning that they will not spike blood sugar as much and require more energy to digest. Consuming these foods and other healthy foods can significantly boost the metabolism and lead to increased fat loss over time.
Balanced diet is essential
A balanced diet is essential for optimal metabolic function. Consuming the right amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can ensure your body functions correctly.
Additionally, consuming specific foods such as green tea, chili peppers, and whole grains can provide an extra boost to metabolic rate, which helps with weight loss goals. Remember that small dietary changes over time lead to more significant results.
Exercise and Metabolism
When it comes to boosting metabolism, exercise is a powerful tool that can help increase your metabolic rate and burn more calories. Exercise not only burns calories during the activity but also helps to build muscle mass, which increases your basal metabolic rate (BMR).
BMR refers to the number of calories your body burns at rest. The more muscle mass you have, the higher your BMR will be, which means you will burn more calories even when not exercising.
Explanation of how exercise affects metabolism
During exercise, your body uses energy to fuel the activity. This energy comes from the food you eat in the form of glucose stored in muscles or glycogen stored in the liver and muscle tissue.
When this energy source is depleted during exercise, your body turns to stored fat for fuel, leading to fat loss. Regular exercise also stimulates the production of hormones such as testosterone which helps boost metabolic rate and aids weight loss.
The effect of exercise on metabolism varies based on factors such as age, fitness level, and type of activity performed. However, studies show that even moderate-intensity aerobic activity can increase metabolic rate several hours after exercising.
Types of exercises that are most effective for boosting metabolic rate
Not all types of exercises are created equal for boosting metabolism. Some varieties are more effective in burning calories and building muscle mass. Aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, or swimming is great for burning calories during physical exertion. In contrast, resistance training, like weightlifting, burns calories and builds lean muscle mass, increasing BMR even while resting.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is another type of workout that is highly effective in increasing metabolism long after the workout. HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest.
The benefits of strength training for increasing muscle mass
Strength training is an important component of any exercise program. It involves using weights or resistance to build muscle mass and increase overall strength.
The benefits of strength training go beyond just aesthetics- it can also help to increase metabolic rate, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of injury during physical activity. An effective strength-training program should include a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups in your body.
These can include squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows. Regularly performing these exercises with proper form and technique can build lean muscle mass, which will help increase metabolism and burn more calories even at rest.
Exercising regularly is an excellent way to boost metabolism by burning calories during the activity and building lean muscles, which increases BMR even while at rest. Resistance training like weightlifting and HIIT are instrumental in achieving this goal as they are highly effective in building muscle mass while burning calories.
Combining Diet & Exercise for Fat Loss
The Importance of Creating a Caloric Deficit through Diet and Exercise to Achieve Fat Loss
Fat loss is achieved by creating a caloric deficit, meaning consuming fewer calories than the body requires to function. This deficit can be made through both diet and exercise.
A combination of both will yield the best results. The human body requires energy to exist, called basal metabolic rate (BMR).
BMR accounts for about 60-70% of daily caloric expenditure. Additional calories are burned through everyday activities such as walking, exercising, and other physical activities.
By creating a caloric deficit, the body is forced to draw on stored fat for energy, leading to fat loss. The recommended daily calorie intake varies based on age, gender, activity level, and muscle mass.
Generally speaking, women require between 1200-2000 calories per day depending on their activity level, while men require between 1500-2500 calories per day depending on their activity level. Reducing calorie intake by 500-1000 calories per day can result in a weight loss of one to two pounds per week.
To create a caloric deficit through exercise, choose activities that burn more calories, such as HIIT workouts or resistance training, rather than low-intensity steady-state (LISS) exercises like walking or jogging. Resistance training helps build lean muscle mass, which increases metabolism helping with long-term weight management.
How to Create a Sustainable Plan that Includes Both Diet and Exercise to Maximize Results
Sustainable weight loss requires choosing a healthy and satisfying eating plan, along with incorporating regular physical activity into your routine. Focusing on short-term and long-term goals is essential when developing a sustainable program.
Start by using an online calculator to determine how many total calories you need each day. Once you have that number, you can calculate your caloric deficit by subtracting 500-1000 calories per day from that number.
Next, plan meals and snacks for the week ahead to ensure you stay within your target calorie range. Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates while avoiding processed or high-calorie foods.
Regarding exercise, aim for at least 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week and strength training at least two days per week. Schedule workouts in advance and treat them like appointments to ensure consistency.
The Role of Consistency in Achieving Long-Term Fat Loss Goals
Consistency is key when it comes to achieving long-term fat loss goals. Even with a well-designed plan, if followed consistently over time, weight loss results will be manageable to obtain or maintain.
Develop habits like meal prepping on weekends or tracking calories using an app to stay consistent with diet goals. When dining out, choose wisely; select options that fit your caloric intake rather than higher calorie choices.
For exercise consistency, create an environment that encourages physical activity; ensure workout clothes are clean and readily available; and set up a designated spot for exercise equipment at home. Also, including accountability partners like a gym buddy or hiring a personal trainer can help make the process more enjoyable while keeping you on track.
Understanding the role of metabolism is crucial
Overall, understanding the role of metabolism in fat loss is crucial for anyone looking to improve their overall health and well-being. While diet and exercise are both critical factors, it’s important to remember that they work together to create a sustainable plan to help you achieve your goals. By incorporating a balanced diet focusing on whole foods and regular exercise that includes cardiovascular activity and strength training, you can boost your metabolism and create a caloric deficit necessary for fat loss.
Consistency is critical when it comes to achieving long-term results. It’s important to remember that small changes over time can significantly improve overall health and body composition.
Don’t expect overnight success but know that every positive step will bring you closer to your goals. There is no magic pill or quick fix for achieving fat loss.
To truly see sustainable results, focus on creating a lifestyle plan with a balanced diet and regular exercise routine. By making these changes over time, you will achieve your desired body composition and improve your overall health and well-being.
Remember: You Got This!
It’s easy to become overwhelmed with all the information about weight loss, diets, supplements, etc. But don’t let this discourage you! Remember why you started in the first place – whether for health reasons or just wanting to look better in your favorite pair of jeans – keep this goal at the forefront of your mind.
You have all the tools necessary for success – motivation, knowledge about metabolism & diet/exercise strategies- so keep pushing forward! Every day presents an opportunity for improvement- whether trying new foods or increasing the intensity of your workout regimen – so embrace the journey toward optimal health & wellness!